In modern network technology, routers are indispensable in both our daily lives and work. Whether for home internet or industrial data transmission, we can’t do without them. With the rise of the “Industrial Internet of Things” concept, the role of routers in industrial fields has become increasingly important. They’re not only key to data transmission but also vital tools for realizing remote device monitoring and automated management. You might have heard the term “industrial router,” but what exactly is it, and how does it differ from the ordinary routers we commonly see? If you’re not quite clear, let’s discuss this in detail.
What is a Router? And What is An Industrial Router?
Nowadays, routers have almost become a necessity in everyone’s life. We use them every day to surf the web on our phones and computers. So, what exactly is a router? Simply put, an ordinary router, also called an internetwork connector, has a core function: connecting to the wide area network (WAN), i.e., the Internet, via a WAN port—this is how we get actual network access. A typical router has up to two WAN ports. It then connects to terminal devices like printers and computers via LAN ports, enabling these devices to access the internet. Routers have limited LAN ports, usually 3-5, which suffice for home use. But to connect more downstream devices, a switch is needed.
An industrial router is essentially similar to a home router, primarily used to connect devices and transmit data. As the name suggests, it’s designed for industrial environments. Its construction is tailored for complex or harsh conditions, such as a wider operating temperature range, sturdier materials, and embedded/rail-mounted installation methods for various onsite scenarios.
Additionally, industrial routers support many functions that ordinary routers don’t, such as cellular connectivity, VPN, serial communication, and other communication methods, as well as extra features like remote management, batch configuration, and OTA (Over-The-Air) updates. In short, industrial routers are more robust, feature-rich, and performant. If anything is unclear, we’ll elaborate below.
Differences Between Industrial and Normal Routers
The differences mainly lie in functionality, performance, design, and usage scenarios. Let’s explore them one by one:
Environmental adaptability
Ordinary routers are designed for home or office use, suitable for temperatures between 0°C and 40°C, and are sensitive to external conditions.
Industrial routers, however, can operate in extreme temperatures from -40°C to +80°C. They also feature dustproof, moisture-proof, lightning-proof designs and strong resistance to electromagnetic interference.
Stability and continuous operation capability
Ordinary routers are suitable for daily use, but prolonged operation may affect their lifespan, requiring regular restarts.
Industrial routers support 7×24-hour non-stop operation, often with self-recovery, auto-restart, and network reconnection features when disconnected. The reason why it is so stable is that in addition to using more reliable industrial-grade chips and components, industrial routers generally support multi-link backup. For example, a dual WAN port router can have two links working at the same time to share network pressure; if a main line is broken, it will automatically switch to the backup link, and it can even switch between cellular and wired Ethernet to achieve redundancy.

Housing material and design
Ordinary routers typically have plastic casings, designed for aesthetics and portability. They’re placed indoors, vulnerable to water and high temperatures.
Industrial routers, however, often use metal or aluminum alloy casings for sturdiness, with dustproof and waterproof ratings (e.g., IP40 for general durability, IP68 for full dust and water protection). They often feature ribbed designs for fanless heat dissipation.
Installation methods
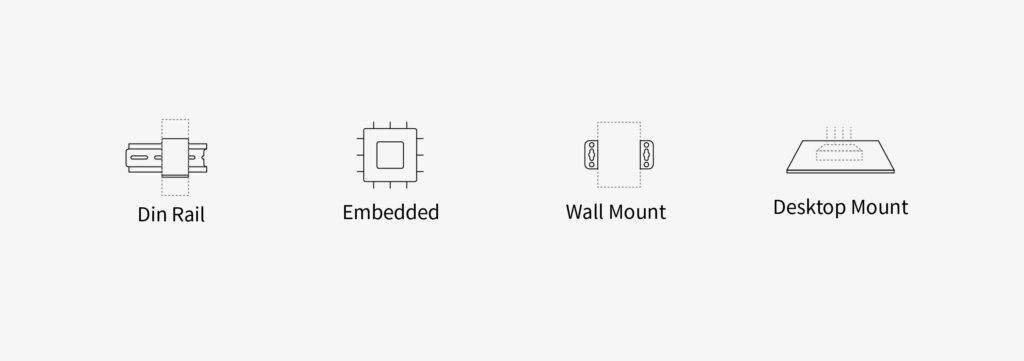
Ordinary routers are usually wall-mounted or desktop-placed—simply hung on a wall or placed on a table/drawer. Industrial routers, due to their usage environments, offer DIN rail and embedded installation methods for industrial sites.
- DIN rail industrial routers can be installed on 35 mm standard rails inside electrical control cabinets, distribution boxes, or communication cabinets.
- Embedded routers are designed as modular boards or ultra-small casings, directly installable on the main device’s shell, panel, or internal space. Some even have no casing, suitable for embedding in explosion-proof boxes or industrial control boxes.
Communication methods
Ordinary routers mainly support wired broadband or Wi-Fi, serving consumer devices like phones and computers. Industrial routers support multiple communication methods, including 4G/5G cellular networks, VPN, and serial communication.
In outdoor scenarios with difficult cabling or temporary setups, industrial cellular routers can connect to 4G/5G networks via SIM cards.
For data confidentiality or remote access to private networks, industrial VPN routers can help.
To connect industrial terminal devices using ports like RS-485, RS-232, M12, instead of standard RJ45 ports, industrial serial routers enable interface conversion.
They also support some industrial protocols like Modbus.

Other functional extensions
The functions of ordinary routers are mainly concentrated on basic Internet access and home network management, and their expansion capabilities are limited.
Industrial routers support advanced functions such as remote management, batch configuration, OTA upgrades, and VPN secure connections. For example, in addition to the VPN functions mentioned above that help us remotely access private networks, encrypt data, and surf the Internet anonymously, the remote management function of industrial routers allows us to remotely view the device operation status through the Web management interface, SNMP protocol or dedicated management platform, such as CPU load, network traffic, temperature sensor data, etc., and remotely debug problems such as link interruption and firmware abnormalities to reduce on-site maintenance costs.
حماية
Security is a key design consideration for network devices. Ordinary routers meet basic security needs, while industrial routers integrate advanced security measures, including Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), VPN, robust user authentication, and data encryption. These suit scenarios with high-security requirements, such as smart manufacturing, energy grids, and intelligent transportation, ensuring stable operation of critical services and security of core data.
Roles and Application Scenarios of Industrial Routers
From the above, industrial routers are designed for complex environments to stably connect terminals to the internet or local area networks. They also provide remote control, data transmission, network backup, and security encryption to solve practical problems.
Thanks to their rich functions and robust performance, industrial routers are widely used in industrial automation, smart grids, traffic monitoring, environmental monitoring, unmanned devices, etc., ensuring 24/7 stable networking and remote management of critical equipment. In daily life, for example, many subway turnstiles and surveillance cameras rely on industrial routers for real-time data upload. Shared charging piles and vending machines on the street often use 4G/5G industrial routers for network access, enabling remote maintenance and billing. What’s more, industrial cellular routers can also be used in the POS networking of some concentrated temporary vendors, which can achieve wireless connection to many devices without complicated wiring. Even smart trash bins and intelligent streetlights in cities can leverage industrial routers for remote data transmission.
خاتمة
Although industrial routers and ordinary routers seem to have similar functions, they are actually very different in terms of application scenarios, design standards, functional stability, etc. In short, ordinary routers are suitable for use in relatively stable places such as homes and offices. Industrial routers are more durable, smarter, more stable, and have more functions. If you are an enterprise user, especially in the fields of industry, energy, transportation, etc., then choosing an industrial-grade router will make your system more reliable, safer, and smarter.